How To Update My Github Repository
Options for getting changes
These commands are very useful when interacting with a remote repository. clone and fetch download remote code from a repository'south remote URL to your local computer, merge is used to merge different people's work together with yours, and pull is a combination of fetch and merge.
Cloning a repository
To catch a complete copy of some other user's repository, utilise git clone like this:
$ git clone https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git # Clones a repository to your computer You tin can choose from several different URLs when cloning a repository. While logged in to GitHub, these URLs are available below the repository details:
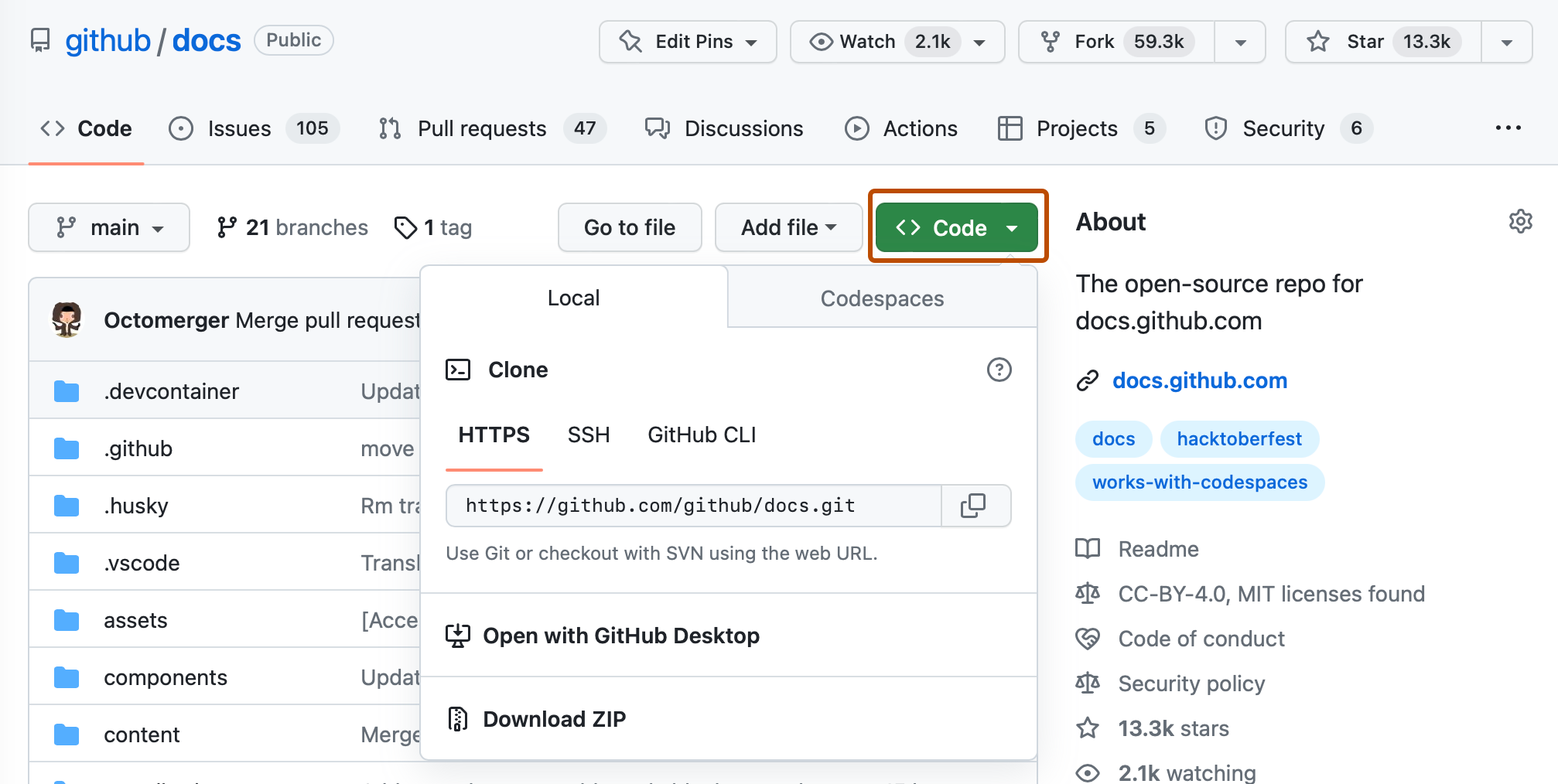
When you run git clone, the post-obit deportment occur:
- A new folder called
repois made - It is initialized as a Git repository
- A remote named
originis created, pointing to the URL you cloned from - All of the repository'southward files and commits are downloaded there
- The default branch is checked out
For every branch foo in the remote repository, a respective remote-tracking branch refs/remotes/origin/foo is created in your local repository. You can usually abbreviate such remote-tracking co-operative names to origin/foo.
Fetching changes from a remote repository
Apply git fetch to think new work washed by other people. Fetching from a repository grabs all the new remote-tracking branches and tags without merging those changes into your own branches.
If yous already have a local repository with a remote URL set up upwards for the desired project, you tin can grab all the new information by using git fetch *remotename* in the terminal:
$ git fetch remotename # Fetches updates made to a remote repository Otherwise, you can always add a new remote and and then fetch. For more information, see "Managing remote repositories."
Merging changes into your local branch
Merging combines your local changes with changes made past others.
Typically, you'd merge a remote-tracking co-operative (i.e., a branch fetched from a remote repository) with your local branch:
$ git merge remotename/branchname # Merges updates made online with your local piece of work Pulling changes from a remote repository
git pull is a convenient shortcut for completing both git fetch and git merge in the aforementioned control:
$ git pull remotename branchname # Grabs online updates and merges them with your local work Because pull performs a merge on the retrieved changes, y'all should ensure that your local work is committed before running the pull command. If yous run into a merge conflict you cannot resolve, or if you make up one's mind to quit the merge, you tin use git merge --abort to take the branch dorsum to where it was in before you pulled.
Further reading
- "Working with Remotes" from the Pro Git book"
- "Troubleshooting connectivity issues"
Source: https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/using-git/getting-changes-from-a-remote-repository
Posted by: soderquistglight.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Update My Github Repository"
Post a Comment